I’m currently spending most of my time explaining to students, hobbyists, professional developers and teachers how to build games using HTML5. Then, I recently thought, rather than keeping all these details for small audiences, wouldn’t it be smarter to share it with you? This article is then based on my own experience. I will probably omit some crucial things some of you may know. But I’ll try to update this post with my own new discoveries and, of course, based on the feedback you kindly provide in the comments or via Twitter.
But why are so many people currently interested in HTML5 Gaming?
Well, simply because today we can really use HTML5 to target multi-platforms using the same code: for desktop machines of course (with IE9/IE10, Firefox, Chrome, Opera and Safari), for iOS and Android tablets and phones and Windows 8 (and its future associated millions of tablets and PCs, is also warmly welcoming HTML5 Games! I then frequently see some HTML5 gaming projects ported to each of these platforms with almost no effort. What’s more, the modern JavaScript engines performance coupled with the GPU hardware-accelerated graphics layers enable us to build great games in HTML5 with confidence. Note: we will only talk about the<canvas> tag of HTML5 and about SVG in this article.
Canvas and SVG: two ways to draw on the screen
 The first thing you need to understand before building your first HTML5 game is how to draw nice objects on the screen. There are two ways to do that and to better understand their differences, you should start by reading this article from Patrick Dengler (member of the SVG W3C Working Group): Thoughts on when to use Canvas and SVG.
You should also look at these two great sessions from MIX11:
– Modernizing Your Website: SVG Meets HTML5
– Deep Dive Into HTML5 <canvas>
Once you have reviewed all this content, you will probably better understand why almost all HTML5 games are using Canvas rather than SVG. Canvas offers a well-known development model for games developers (low level drawing APIs) and is now very well hardware-accelerated by most of the recent browsers. Still SVG, and its vectors-based technology, is naturally better armed to scale across devices without losing quality. You just need to use the magic ViewBox property of SVG, which will handle that for you. Your games assets will then scale from 3″ to 80″ screens in a very easy way!
Sometimes, it is even possible to achieve the exact same game using both technologies. For instance, here is the same simple game first using SVG then Canvas: SVG Racketball and Canvas Racquetball. They both came out of this MSDN documentation: Programming Simple Games Using Canvas or SVG.
In this case, analyzing the performance of each technology could help you to decide which one to use for your game. For instance, here are two interesting experiments that will display a thousand small balls on your screen using SVG: 1000 balls in SVG and using Canvas: 1000 balls in Canvas. Test both experiments in your favorite browser. In general, the Canvas performance is better for drawing a lot of objects on the screen, in this particular case. But this is generally also what we’d like to achieve in our video games. To have a better overview of the performance comparison, here is an interesting diagram to look at:
The first thing you need to understand before building your first HTML5 game is how to draw nice objects on the screen. There are two ways to do that and to better understand their differences, you should start by reading this article from Patrick Dengler (member of the SVG W3C Working Group): Thoughts on when to use Canvas and SVG.
You should also look at these two great sessions from MIX11:
– Modernizing Your Website: SVG Meets HTML5
– Deep Dive Into HTML5 <canvas>
Once you have reviewed all this content, you will probably better understand why almost all HTML5 games are using Canvas rather than SVG. Canvas offers a well-known development model for games developers (low level drawing APIs) and is now very well hardware-accelerated by most of the recent browsers. Still SVG, and its vectors-based technology, is naturally better armed to scale across devices without losing quality. You just need to use the magic ViewBox property of SVG, which will handle that for you. Your games assets will then scale from 3″ to 80″ screens in a very easy way!
Sometimes, it is even possible to achieve the exact same game using both technologies. For instance, here is the same simple game first using SVG then Canvas: SVG Racketball and Canvas Racquetball. They both came out of this MSDN documentation: Programming Simple Games Using Canvas or SVG.
In this case, analyzing the performance of each technology could help you to decide which one to use for your game. For instance, here are two interesting experiments that will display a thousand small balls on your screen using SVG: 1000 balls in SVG and using Canvas: 1000 balls in Canvas. Test both experiments in your favorite browser. In general, the Canvas performance is better for drawing a lot of objects on the screen, in this particular case. But this is generally also what we’d like to achieve in our video games. To have a better overview of the performance comparison, here is an interesting diagram to look at:
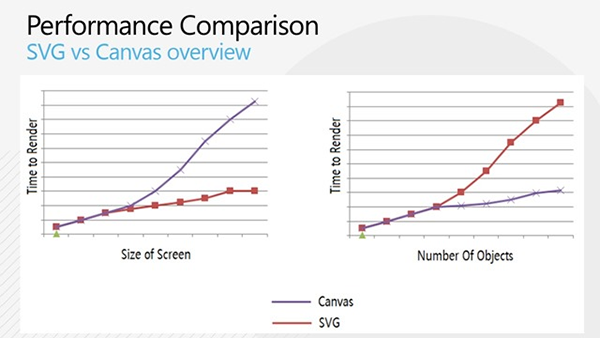 But nothing prevents you from mixing both technologies. Indeed, we could perfectly imagine using a first layer based on SVG to display the game menus with a second layer in background using a canvas for the game itself. You will then use what we call the browser compositing engine. However, you must pay real attention to final performance results because the browsers and devices are far from being equals in this domain. Don’t forget that the main interest of HTML5 is to target all platforms.
My colleague David Catuhe has created a couple of months ago a little brick breaker game using this composition principle: How to write a small game using HTML5 and JavaScript–BrikBrok . The first layer is using SVG for the bricks to break and the background can display a tunnel effect using the canvas tag. You can perfectly mimic this concept to display the main game in background (hosting a platformer or shoot’em up game, etc.) instead of the tunnel and your first layer will simply display the menus and configuration options in SVG.
But nothing prevents you from mixing both technologies. Indeed, we could perfectly imagine using a first layer based on SVG to display the game menus with a second layer in background using a canvas for the game itself. You will then use what we call the browser compositing engine. However, you must pay real attention to final performance results because the browsers and devices are far from being equals in this domain. Don’t forget that the main interest of HTML5 is to target all platforms.
My colleague David Catuhe has created a couple of months ago a little brick breaker game using this composition principle: How to write a small game using HTML5 and JavaScript–BrikBrok . The first layer is using SVG for the bricks to break and the background can display a tunnel effect using the canvas tag. You can perfectly mimic this concept to display the main game in background (hosting a platformer or shoot’em up game, etc.) instead of the tunnel and your first layer will simply display the menus and configuration options in SVG.
Useful libraries and tools
Graphics
Writing the XML nodes of SVG manually or even playing with the low level APIs of Canvas could be fun for a moment but not very productive. Here is then a useful set of tools and libraries I like that could help you build parts of your HTML5 game. To generate some SVG, here are some cool tools: – InkScape: a free and open source desktop software – SVG Editor: an online software running directly inside your browser Adobe Illustrator also supports SVG as an export target but it’s a bit more expensive. ;-) If you’re looking for your game assets (for menus or controls), you should have a look at this free icons library: The Noun Project. So if you’re not lucky enough to work with a designer, it could save you. There is another library with some free SVG content also here: Open Clip Art Library. To conclude on SVG, THE ultimate library you have to know is named RaphaelJS. It’s a JavaScript library that will help you generate dynamic SVG with a few lines of code. You’ll find a lot of cool demos on the website using for instance nonlinear animation functions on SVG elements, animated charts, etc. But if you’re looking specifically for charting (let’s say to display some players’ stats), THE ultimate charting library is named HighCharts. Those two libraries are so awesome that they even implement VML fallbacks for IE8 or older versions. But this shouldn’t be something to worry about if you’re building HTML5 games. You’ll probably target at least IE9 and above.
 If you’d like to display charts using Canvas, I’m a huge fan of the JavaScript InfoVis Toolkit library. Just have a look at the demos on their website, it’s just awesome and simple to use.
If you’d like to display charts using Canvas, I’m a huge fan of the JavaScript InfoVis Toolkit library. Just have a look at the demos on their website, it’s just awesome and simple to use.
 Let’s continue on the graphics side. There is a very well-known library built to simplify the usage of 3D in JavaScript named ThreeJS. Most of the time, it is used to render some hardware-accelerated 3D via WebGL. But you can ask for a rendering inside the 2D canvas element of HTML5. For that, simply check the “CanvasRenderer examples” section of the site. This is the library we’ve used, for instance, to build our Galactic demo on the IE Test Drive. Using the “CanvasRenderer”, you can then build 3D scenes working in all HTML5 browsers. Something that could be good to know.
Note: we can also combine all of these graphics effects with the usage of CSS3 2D and 3D Transforms coupled with transitions or animations in your game. But I’ve decided to stay focused on Canvas and SVG in this article.
Let’s continue on the graphics side. There is a very well-known library built to simplify the usage of 3D in JavaScript named ThreeJS. Most of the time, it is used to render some hardware-accelerated 3D via WebGL. But you can ask for a rendering inside the 2D canvas element of HTML5. For that, simply check the “CanvasRenderer examples” section of the site. This is the library we’ve used, for instance, to build our Galactic demo on the IE Test Drive. Using the “CanvasRenderer”, you can then build 3D scenes working in all HTML5 browsers. Something that could be good to know.
Note: we can also combine all of these graphics effects with the usage of CSS3 2D and 3D Transforms coupled with transitions or animations in your game. But I’ve decided to stay focused on Canvas and SVG in this article.
Physics Engine
Of course, displaying graphics is far from being the only task you need to do in a game. There is also the AI (Artificial Intelligence) you need to code to bring life to your characters. Unfortunately, you will need to code that alone and be creative. But you will be glad to know you don’t need to worry about the physics and collisions part of your game. Simply learn to how to use Box2D JS. Go play with the various samples and you’ll be amazed: If you’re interested in this topic, you should then read the excellent tutorial series by Seth Ladd here: Box2D orientation for the JavaScript developer . Seth even used the Web Workers to compute the physics on the several available cores of your CPU. If you don’t know what the Web Workers are, I’ve written an introduction on these new APIs here: Introduction to the HTML5 Web Workers: the JavaScript multithreading approach. It could be useful in certain scenarios for your games.
If you’re interested in this topic, you should then read the excellent tutorial series by Seth Ladd here: Box2D orientation for the JavaScript developer . Seth even used the Web Workers to compute the physics on the several available cores of your CPU. If you don’t know what the Web Workers are, I’ve written an introduction on these new APIs here: Introduction to the HTML5 Web Workers: the JavaScript multithreading approach. It could be useful in certain scenarios for your games.
Handling the multi touch events
If you’d like to build a cross-devices game, you will have to support touch. Currently, there are two existing specifications around Touch Events. So there is no official standard one yet. If you’d like to know a bit more about why, here is an interesting article: Getting Touchy About Patents You will need to write code that works fine in IE10 and Windows 8 as well as with the implementation coming from the Apple devices. For that, you should definitely have a look at this sample demonstrating a possible pattern to support both kind of touch events: Finger Painting and its associated article: Handling Multi-touch and Mouse Input in All Browsers. But if you’re interesting in checking how far you can now go by handling multi-touch inside IE10, test this cool demo: Browser Surface . You’ll need a recent IE10 version and multitouch hardware running it.
Boris Smus has started working for his part on a library named Pointer.js. The idea is to consolidate all types of touch (IE10, iOS like, mouse and pen) to simplify your developer life. You can read his article about that here: Generalized input on the cross-device web. Currently, the library is just a draft and doesn’t support yet the MSPointer* of IE10. So feel free to contribute to the project to help him! (I’ve planned to try to help him when I have some spare time)
You will need to write code that works fine in IE10 and Windows 8 as well as with the implementation coming from the Apple devices. For that, you should definitely have a look at this sample demonstrating a possible pattern to support both kind of touch events: Finger Painting and its associated article: Handling Multi-touch and Mouse Input in All Browsers. But if you’re interesting in checking how far you can now go by handling multi-touch inside IE10, test this cool demo: Browser Surface . You’ll need a recent IE10 version and multitouch hardware running it.
Boris Smus has started working for his part on a library named Pointer.js. The idea is to consolidate all types of touch (IE10, iOS like, mouse and pen) to simplify your developer life. You can read his article about that here: Generalized input on the cross-device web. Currently, the library is just a draft and doesn’t support yet the MSPointer* of IE10. So feel free to contribute to the project to help him! (I’ve planned to try to help him when I have some spare time)
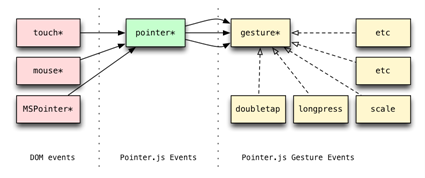
Building connected games
If you’d like to build multiplayer games or simply a game connected to a server for any reason, you’ll naturally be interested in using WebSockets. This W3C specification (and the underlying protocol handled by the IETF) is indeed stable enough to start to be used in production. But if you’d like to support the widest possible number of users, you need to consider a fallback for browsers or devices which aren’t supporting WebSockets yet or support an older, deprecated version. We might dream of solutions like automatically falling back to an older method of pooling or long pooling for browsers like IE9, and offering Web Sockets to more recent browsers like IE10. And yes, could it be possible also to have a unique code handling that?
Well, stop dreaming: the community made it. There are two solutions I know of doing that:
– the Socket.IO library for Node.js
– SignalR working on top of IIS and ASP.NET
Both libraries will help you to handle all the browsers and devices with their variety of support levels.
Some gaming frameworks
To build a 2D HTML5 game, there are several things you need to care about:
1 – Handling your sprites: splitting them into a sequence, animating them, effects, etc.
2 – Handling your sounds and music (and this is not always easy in HTML5!)
3 – Loading asynchronously your assets from the web server via a dedicated loader/assets manager
4 – Building a collision engine, a high level logic for your game objects, etc.
Well, you can either do that starting from scratch or you can test and review what other brilliant developers have already done on the web. I’d definitely advise you to take the second option as the JS gaming frameworks start to really mature and be tested in games in production.
As there is a ton of JS gaming frameworks on the web (well, there is a ton of anything .JS actually), here are the best-known frameworks to build HTML5 2D games working inside all browsers:
– MelonJS : a free framework that exposes a lot of useful services. Its big advantage is that it works fine with the Tiled Map Editor tool.
– CraftyJS that I unfortunately don’t know very well
– ImpactJS : a high quality well-known framework. It’s not free but not too expensive.
– EaselJS : my favorite one! Written by an old Flash developer. So if you have written some games in Flash, you should feel at home with this framework. It’s part of the CreateJS suite. It’s very complete, well documented and… free.
So, you should now be warned. As EaselJS is the framework I know the most, I won’t be impartial. It’s up to you to test the others and form your own opinion.
But if you’d like to support the widest possible number of users, you need to consider a fallback for browsers or devices which aren’t supporting WebSockets yet or support an older, deprecated version. We might dream of solutions like automatically falling back to an older method of pooling or long pooling for browsers like IE9, and offering Web Sockets to more recent browsers like IE10. And yes, could it be possible also to have a unique code handling that?
Well, stop dreaming: the community made it. There are two solutions I know of doing that:
– the Socket.IO library for Node.js
– SignalR working on top of IIS and ASP.NET
Both libraries will help you to handle all the browsers and devices with their variety of support levels.
Some gaming frameworks
To build a 2D HTML5 game, there are several things you need to care about:
1 – Handling your sprites: splitting them into a sequence, animating them, effects, etc.
2 – Handling your sounds and music (and this is not always easy in HTML5!)
3 – Loading asynchronously your assets from the web server via a dedicated loader/assets manager
4 – Building a collision engine, a high level logic for your game objects, etc.
Well, you can either do that starting from scratch or you can test and review what other brilliant developers have already done on the web. I’d definitely advise you to take the second option as the JS gaming frameworks start to really mature and be tested in games in production.
As there is a ton of JS gaming frameworks on the web (well, there is a ton of anything .JS actually), here are the best-known frameworks to build HTML5 2D games working inside all browsers:
– MelonJS : a free framework that exposes a lot of useful services. Its big advantage is that it works fine with the Tiled Map Editor tool.
– CraftyJS that I unfortunately don’t know very well
– ImpactJS : a high quality well-known framework. It’s not free but not too expensive.
– EaselJS : my favorite one! Written by an old Flash developer. So if you have written some games in Flash, you should feel at home with this framework. It’s part of the CreateJS suite. It’s very complete, well documented and… free.
So, you should now be warned. As EaselJS is the framework I know the most, I won’t be impartial. It’s up to you to test the others and form your own opinion.
Some beginners’ tutorials
Well, being the pure megalomaniac I am, let me start by sharing with you my own tutorials. A year ago, I had fun porting an XNA C# game into HTML5/JavaScript thanks to EaselJS. I then decided to write three initial tutorials to share this experience: – HTML5 Gaming: animating sprites in Canvas with EaselJS – HTML5 Gaming: building the core objects and handling collisions with EaselJS – HTML5 Platformer: the complete port of the XNA game to <canvas> with EaselJS Several months later, I added three other articles enhancing/extending the same game: – Tutorial: how to create HTML5 applications on Windows Phone thanks to PhoneGap where I’ll show you how to port the same game on Windows Phone thanks to PhoneGap/Cordova. But you will be able to follow the same instructions for your Android or iOS device. – Modernizing your HTML5 Canvas games Part 1: hardware scaling and CSS3 where we’ll use CSS3 3D Transform, Transitions and Grid Layout to enhance the gaming experience – Modernizing your HTML5 Canvas games Part 2: Offline API, Drag’n’drop and File API where we will enable playing to the game in offline mode. You will be even able to create your own levels and drag’n’drop them directly into the game. After following them, you’ll build this game: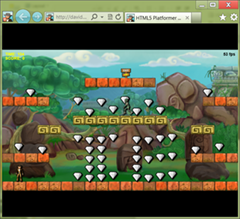 Well, logically, thanks to these six tutorials, you should be able to write your own HTML5 game whatever the browser or device you’re targeting.
You’ll find also a lot of simple demo to understand and great tutorials on the EaselJS website: http://www.createjs.com/#!/EaselJS as well as on each framework’s website mentioned above.
You’ll also find more generic tutorials on these sites:
– HTML5 Game Dev Tutorials
– 10 cool HTML5 games and how to create your own
To conclude, I’d like to recommend to you two more “advanced” articles, but very instructive to read. The first one is written by David Catuhe from Microsoft: Unleash the power of HTML 5 Canvas for gaming . He will share with you some optimization he has found while working on a “demo” like the one we were writing in the “demo scene”. The tips found could bring you some ideas for your own HTML5 games. The second one is written again by Boris Smus from Google: Improving HTML5 Canvas Performance and it contains a ton of good advice.
Some interesting online working games and experience feedbacks
Again, this is my personal favorite. You will probably find other cool examples on the web to share. Whatever the game you like, it is interesting to analyze how the developers made them. Thanks to the magic of the web, you just have to right-click and “view source”. Even if the code will be probably minified, you can still learn a couple of interesting things by looking at the global architecture of the game.
Let’s start by some productions using the EaselJS framework. The first one was Pirates Love Daisies written by Grant Skinner:
Well, logically, thanks to these six tutorials, you should be able to write your own HTML5 game whatever the browser or device you’re targeting.
You’ll find also a lot of simple demo to understand and great tutorials on the EaselJS website: http://www.createjs.com/#!/EaselJS as well as on each framework’s website mentioned above.
You’ll also find more generic tutorials on these sites:
– HTML5 Game Dev Tutorials
– 10 cool HTML5 games and how to create your own
To conclude, I’d like to recommend to you two more “advanced” articles, but very instructive to read. The first one is written by David Catuhe from Microsoft: Unleash the power of HTML 5 Canvas for gaming . He will share with you some optimization he has found while working on a “demo” like the one we were writing in the “demo scene”. The tips found could bring you some ideas for your own HTML5 games. The second one is written again by Boris Smus from Google: Improving HTML5 Canvas Performance and it contains a ton of good advice.
Some interesting online working games and experience feedbacks
Again, this is my personal favorite. You will probably find other cool examples on the web to share. Whatever the game you like, it is interesting to analyze how the developers made them. Thanks to the magic of the web, you just have to right-click and “view source”. Even if the code will be probably minified, you can still learn a couple of interesting things by looking at the global architecture of the game.
Let’s start by some productions using the EaselJS framework. The first one was Pirates Love Daisies written by Grant Skinner:
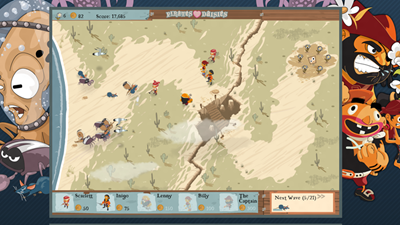 Grant has started his EaselJS framework while building this HTML5 game.
Windows 8 note: you’ll notice you’ll find the very same game working inside Windows 8 in the Windows Store here: Pirates Love Daisies for Windows 8 . Indeed, if you have a HTML5 game working fine inside IE9 or IE10, building the Windows 8 version is almost only doing a simple copy and paste! The game will then directly work inside the Windows 8 App experience. But to make a real good Windows 8 game, you will have also to pay attention to the unique Windows 8 experience we’re building. This is described here: Designing great games for Windows
Another game using EaselJS is BKOM ROBOT GAME which uses 3D sprites I love:
Grant has started his EaselJS framework while building this HTML5 game.
Windows 8 note: you’ll notice you’ll find the very same game working inside Windows 8 in the Windows Store here: Pirates Love Daisies for Windows 8 . Indeed, if you have a HTML5 game working fine inside IE9 or IE10, building the Windows 8 version is almost only doing a simple copy and paste! The game will then directly work inside the Windows 8 App experience. But to make a real good Windows 8 game, you will have also to pay attention to the unique Windows 8 experience we’re building. This is described here: Designing great games for Windows
Another game using EaselJS is BKOM ROBOT GAME which uses 3D sprites I love:
 The two most currently famous HTML5 games are of course Angry Birds (which uses the Box2D library I was mentioning above):
The two most currently famous HTML5 games are of course Angry Birds (which uses the Box2D library I was mentioning above):
 And Cut The Rope:
And Cut The Rope:
 You’ll find also a Windows 8 version of it in the Windows Store here: Cut The Rope for Windows 8
It was very simple to port into Windows 8. Here is the process:
1 – Copy/Paste the Web version into a HTML5 Style App project for Windows 8
2 – Add support for touch
3 – Add support for the snapped view and pause the game
4 – Build some High Resolution assets (1366×768 and 1920×1080) to propose the best experience for all the incoming Windows 8 tablets and PC.
I also love the story around “Cut The Rope”. It’s very interesting to read. This was a successful game written in Objective-C for the Apple iOS devices. It was ported into HTML5/Canvas.
I’ve also had pleasure reading this experience feedback: Wooga’s HTML5 Adventure.
Finally, here is a list of 40 more or less good HTML5 games: 40 Addictive Web Games Powered by HTML5 with some others available also here: HTML5games.com
I now hope that all these resources will help you to build your own HTML5 game. If you’re doing so and/or if you have any suggestions to provide on good frameworks/tutorials/concepts you’d like to share, please share your thoughts with me!
If you enjoyed reading this post, you’ll love Learnable; the place to learn fresh skills and techniques from the masters. Members get instant access to all of SitePoint’s ebooks and interactive online courses, like Learn HTML5.
You’ll find also a Windows 8 version of it in the Windows Store here: Cut The Rope for Windows 8
It was very simple to port into Windows 8. Here is the process:
1 – Copy/Paste the Web version into a HTML5 Style App project for Windows 8
2 – Add support for touch
3 – Add support for the snapped view and pause the game
4 – Build some High Resolution assets (1366×768 and 1920×1080) to propose the best experience for all the incoming Windows 8 tablets and PC.
I also love the story around “Cut The Rope”. It’s very interesting to read. This was a successful game written in Objective-C for the Apple iOS devices. It was ported into HTML5/Canvas.
I’ve also had pleasure reading this experience feedback: Wooga’s HTML5 Adventure.
Finally, here is a list of 40 more or less good HTML5 games: 40 Addictive Web Games Powered by HTML5 with some others available also here: HTML5games.com
I now hope that all these resources will help you to build your own HTML5 game. If you’re doing so and/or if you have any suggestions to provide on good frameworks/tutorials/concepts you’d like to share, please share your thoughts with me!
If you enjoyed reading this post, you’ll love Learnable; the place to learn fresh skills and techniques from the masters. Members get instant access to all of SitePoint’s ebooks and interactive online courses, like Learn HTML5.
Frequently Asked Questions about HTML5 Games with Canvas and SVG
What are the basic tools needed to start building HTML5 games with Canvas and SVG?
To start building HTML5 games with Canvas and SVG, you need a text editor, a modern web browser for testing, and a basic understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Text editors like Sublime Text, Atom, or Visual Studio Code are great for writing your code. Modern browsers like Chrome, Firefox, or Safari have built-in developer tools that can help you debug your code. Lastly, knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is crucial as these are the building blocks of your game.
How can I animate objects in HTML5 games?
Animation in HTML5 games is achieved through the use of the Canvas API’s requestAnimationFrame method. This method tells the browser to perform an animation and requests that the browser call a specified function to update an animation before the next repaint. This results in smoother animations compared to using setInterval or setTimeout.
How can I handle user input in HTML5 games?
User input in HTML5 games is typically handled through event listeners. You can listen for keyboard events like ‘keydown’ or ‘keyup’ to move a character, or mouse events like ‘click’ or ‘mousemove’ to shoot a bullet or drag an object. The event object passed to your event handler function contains useful information like the key code or mouse position.
How can I add sound effects to my HTML5 game?
Sound effects can be added to HTML5 games using the Audio API. You can create a new Audio object, set its src attribute to the URL of your sound file, and call the play method to play the sound. You can also control the volume, loop the sound, and listen for events like ‘ended’ or ‘canplay’.
How can I create a game loop in HTML5?
A game loop in HTML5 can be created using the requestAnimationFrame method. This method calls a function you provide to update your game state and redraw the game screen before the next repaint. The game loop is the heartbeat of your game, ensuring that the game state is updated and the screen is redrawn at a smooth and consistent rate.
How can I detect collisions in my HTML5 game?
Collision detection in HTML5 games can be done in several ways, depending on the complexity of your game. For simple games, you can use bounding box collision detection, where you check if the bounding boxes of two objects overlap. For more complex games, you might need to use pixel-perfect collision detection or a physics engine.
How can I optimize my HTML5 game for better performance?
There are several ways to optimize your HTML5 game for better performance. You can use requestAnimationFrame for smoother animations, use offscreen canvases to reduce redraws, use web workers to run heavy computations in the background, and use the performance API to measure and improve your game’s performance.
How can I make my HTML5 game responsive and mobile-friendly?
Making your HTML5 game responsive and mobile-friendly involves designing your game to adapt to different screen sizes and input methods. You can use CSS media queries to adjust your game layout for different screen sizes, and handle touch events in addition to mouse and keyboard events for mobile devices.
How can I save and load game state in HTML5 games?
Saving and loading game state in HTML5 games can be done using the Web Storage API. This API provides two objects, localStorage and sessionStorage, which you can use to store key-value pairs. You can save your game state as a JSON string and load it back when the game starts.
How can I debug my HTML5 game?
Debugging your HTML5 game can be done using the developer tools built into your web browser. These tools allow you to inspect your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code, set breakpoints, step through your code, watch variables, and see any errors or warnings. You can also use console.log statements to log information to the console.
 David Rousset
David RoussetDavid Rousset is a Senior Program Manager at Microsoft, in charge of driving adoption of HTML5 standards. He has been a speaker at several famous web conferences such as Paris Web, CodeMotion, ReasonsTo or jQuery UK. He’s the co-author of the WebGL Babylon.js open-source engine. Read his blog on MSDN or follow him on Twitter.


