A barcode is a machine readable image that encapsulates some data about the object to which it’s attached to. A Quick Response Code (QR Code) is a popular type of barcode for mobile use due to its fast readability and greater storage capacity compared to ordinary barcodes.
In this tutorial I will create a Cordova app which can scan QR Codes and store data obtained from decoding the QR Codes. To scan the barcode I will use the BarcodeScanner Cordova plugin.
Overview of Barcodes
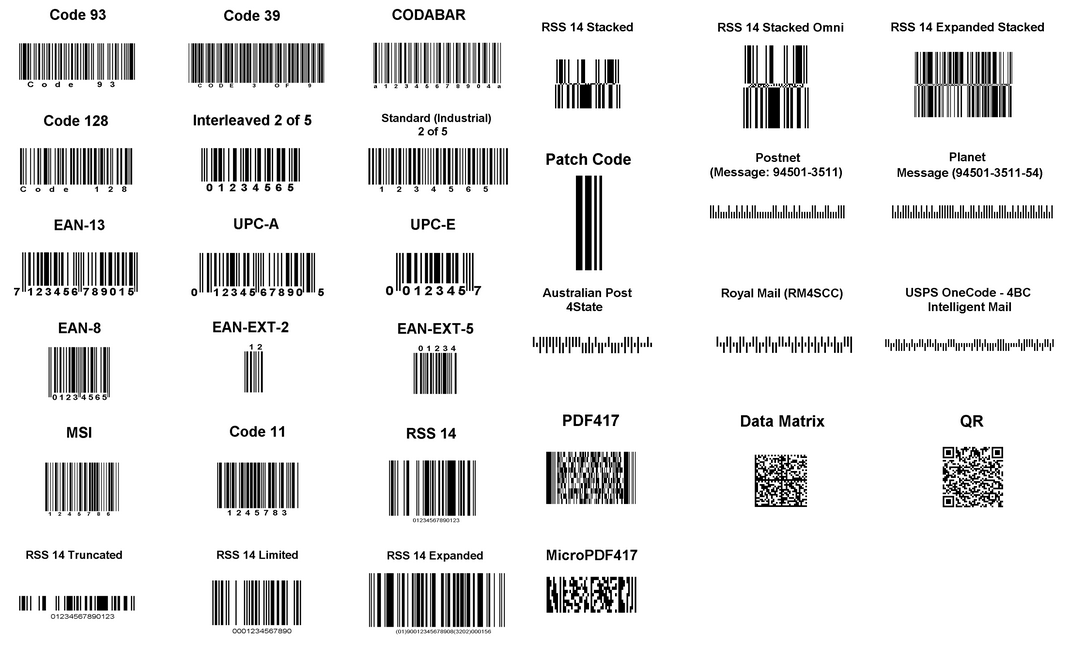
Barcodes are structured images that can be 1D or 2D. 1D barcodes comprise of parallel lines with different heights, widths and colors. 2D barcodes comprise of dots, hexagons and other geometric figures.
Barcodes were originally scanned using special optical scanners called barcode readers. But now we can scan barcodes using devices such as smartphones and printers.
Barcodes are of many different types depending on dimensions, geometric figures and the types of data it can encapsulate. Here are some of the most common types of barcodes:
QR Code
QR codes are one of the most popular types of barcodes in use today, with the ability to encode up to 4296 characters. A QR Code is 2D as you can see in the above image.
Typical QR code applications include product tracking, item identification, time tracking, document management, general marketing, URL sharing, package tracking and much more.
There are several types of QR codes, Model 1, Micro, IQR, SQRC and LogoQ. Model 1 is the most common type and it’s the one I will be using in this app example.
QR codes are widely used on websites where they generally represent the URL of the website. When someone wants to read the content of your web page on their mobile phone, they can scan the QR code which then opens the URL in a browser instead of manually typing a long URL.
The app we will create in this tutorial can be used to scan and store QR Codes that are URLs. It lets you open the URLs inside the app using an InAppBrowser window.
BarcodeScanner Cordova Plugin
The BarcodeScanner Cordova plugins lets you scan and decode different types of barcodes. The plugin works on Android, iOS, Windows and Blackberry platforms.
Here is the basic code that shows how to launch the camera app and scan a barcode using the BarcodeScanner Cordova plugin:
cordova.plugins.barcodeScanner.scan(
function (result) {
if(!result.cancelled)
{
alert("Barcode type is: " + result.format);
alert("Decoded text is: " + result.text);
}
else
{
alert("You have cancelled scan");
}
},
function (error) {
alert("Scanning failed: " + error);
}
);Creating a QR Code Scanner App
Let’s get started with building a QR Code scanner app. This app will let you scan and store QR Codes that are URLs. It also lets you open the URLs inside the app using InAppBrowser window.
You can find the final code of this project on gitHub.
Starting
I won’t cover installing and creating a Cordova Application, if you haven’t done this before, read the getting started guide. Instructions to run and build the application are available on the same page.
Give the Application an appropriate name and add the platforms you want to support.
As I will be using BarcodeScanner, Dialog and InAppBrowser plugins, install them by running the commands below in the Cordova project directory:
cordova plugin add phonegap-plugin-barcodescanner
cordova plugin add org.apache.cordova.dialogs
cordova plugin add org.apache.cordova.inappbrowserInside the www/index.html file, add the following JavaScript and CSS files before the closing body tag:
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-2.1.4.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/mobile/1.4.5/jquery.mobile-1.4.5.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="cordova.js"></script>Remove the current:
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/index.js"></script>Here I added jQuery and jQuery Mobile from CDNs. You can embed these files locally so that the app works without an Internet connection.
Depending on the platform you are building for you may need to change this line:
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src 'self' data: gap: https://ssl.gstatic.com 'unsafe-eval'; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; media-src *">See the comments above this line auto-generated by Cordova for guidance.
Note: All JavaScript code from here onwards should also be placed in a script tag before the closing body tag.
Initialize
We will be storing the scanned data using HTML5 local storage. Place this code in a script tag to initialize the local storage if it hasn’t been already:
if(localStorage.getItem("LocalData") == null)
{
var data = [];
data = JSON.stringify(data);
localStorage.setItem("LocalData", data);
}Here I am storing an empty array. Each array element will be another array with the data name and value that’s scanned.
Creating the Home Screen
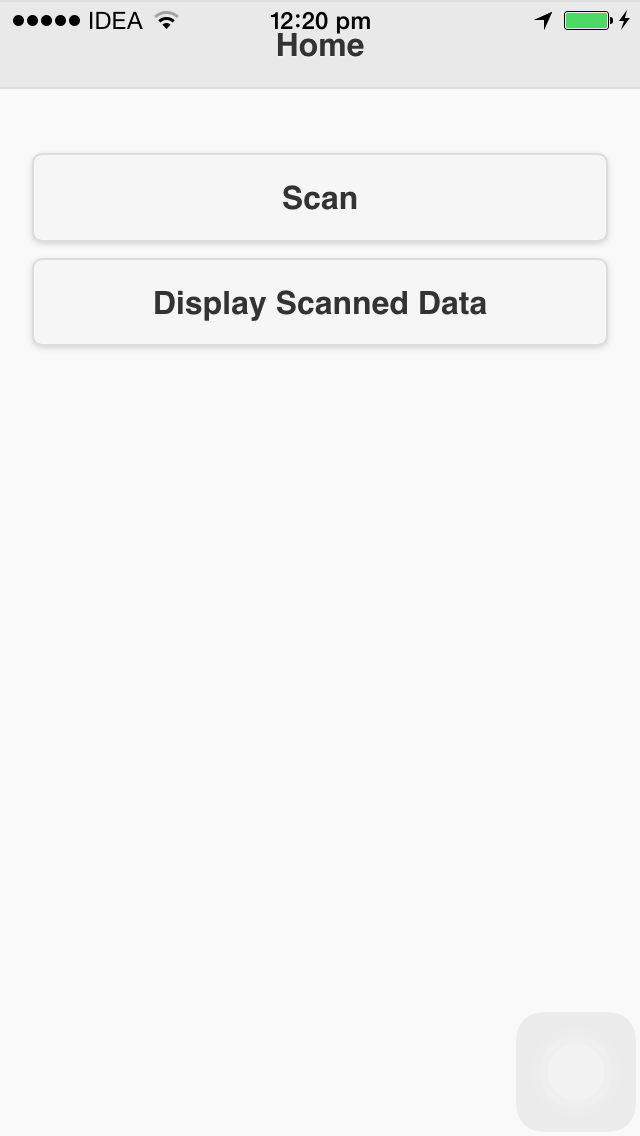
Let’s create a home screen which will display when the app loads.
On the home screen are two buttons. These are for scanning and displaying data.
Place this code in the body tag of the index.html page (Replacing the divs that are there):
<div data-role="page" id="home">
<div data-role="header">
<h1>Home</h1>
</div>
<div data-role="main" class="ui-content">
<p>
<a target="_blank" href="javascript:scan();" style="text-decoration: none"><button>Scan</button></a>
<a target="_blank" href="#display" style="text-decoration: none"><button>Display Scanned Data</button></a>
</p>
</div>
</div>Here is how the page looks:
Scanning
When a user clicks on the Scan button a function named scan() is called. Here is the scan function. Place it inside a script tag:
function scan()
{
cordova.plugins.barcodeScanner.scan(
function (result) {
if(!result.cancelled)
{
if(result.format == "QR_CODE")
{
navigator.notification.prompt("Please enter name of data", function(input){
var name = input.input1;
var value = result.text;
var data = localStorage.getItem("LocalData");
console.log(data);
data = JSON.parse(data);
data[data.length] = [name, value];
localStorage.setItem("LocalData", JSON.stringify(data));
alert("Done");
});
}
}
},
function (error) {
alert("Scanning failed: " + error);
}
);
}Here I am checking the type of barcode once the user has scanned it. If the barcode is a QR Code, then we progress further, otherwise we do nothing.
If the barcode type is a QR Code then we ask the user to input a name to identify the scanned text and store it in local storage. Finally we display an alert box with text Done
.
Here is how the screen looks when the Scan button is first clicked:

Displaying
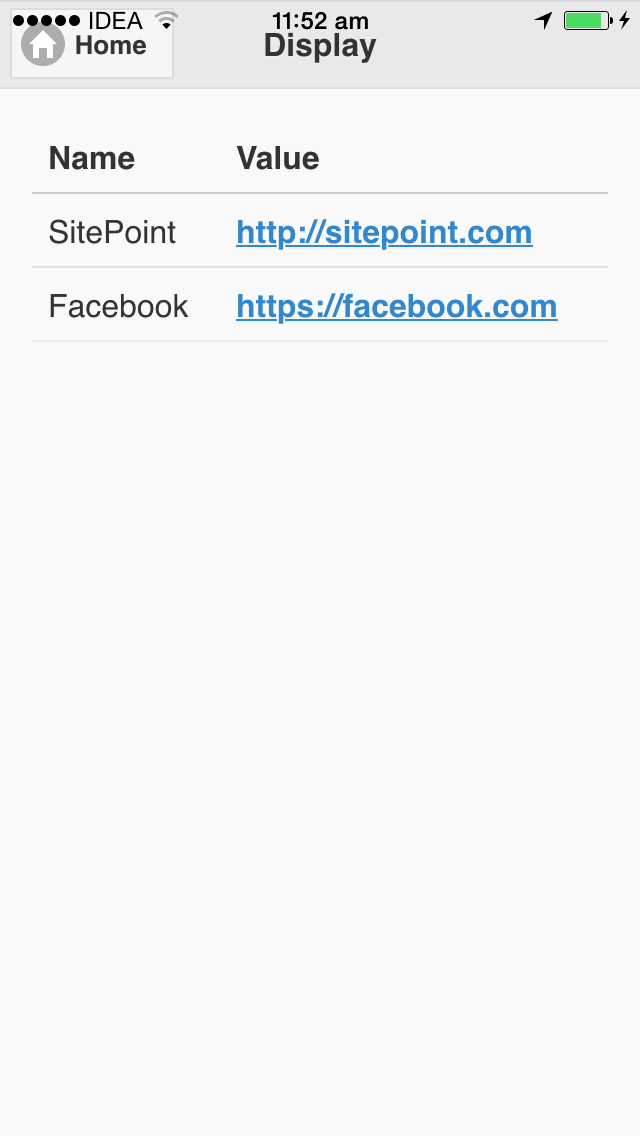
When a user clicks on the Display Data button, it switches to the page with the id display.
Let’s create that page. Place this code inside the body tag:
<div data-role="page" id="display">
<div data-role="header">
<a target="_blank" href="#home" class="ui-btn ui-icon-home ui-btn-icon-left">Home</a>
<h1>Display</h1>
</div>
<div data-role="main" class="ui-content">
<table data-role="table" data-mode="column" id="allTable" class="ui-responsive table-stroke">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Value</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>Here we display an empty table. To populate the table with local storage data, place this code in the script tag:
$(document).on("pagebeforeshow", "#display", function() {
$("table#allTable tbody").empty();
var data = localStorage.getItem("LocalData");
console.log(data);
data = JSON.parse(data);
var html = "";
for(var count = 0; count < data.length; count++)
{
html = html + "<tr><td>" + data[count][0] + "</td><td><a href='javascript:openURL(\"" + data[count][1] + "\")'>" + data[count][1] + "</a></td></tr>";
}
$("table#allTable tbody").append(html).closest("table#allTable").table("refresh").trigger("create");
});
function openURL(url)
{
window.open(url, '_blank', 'location=yes');
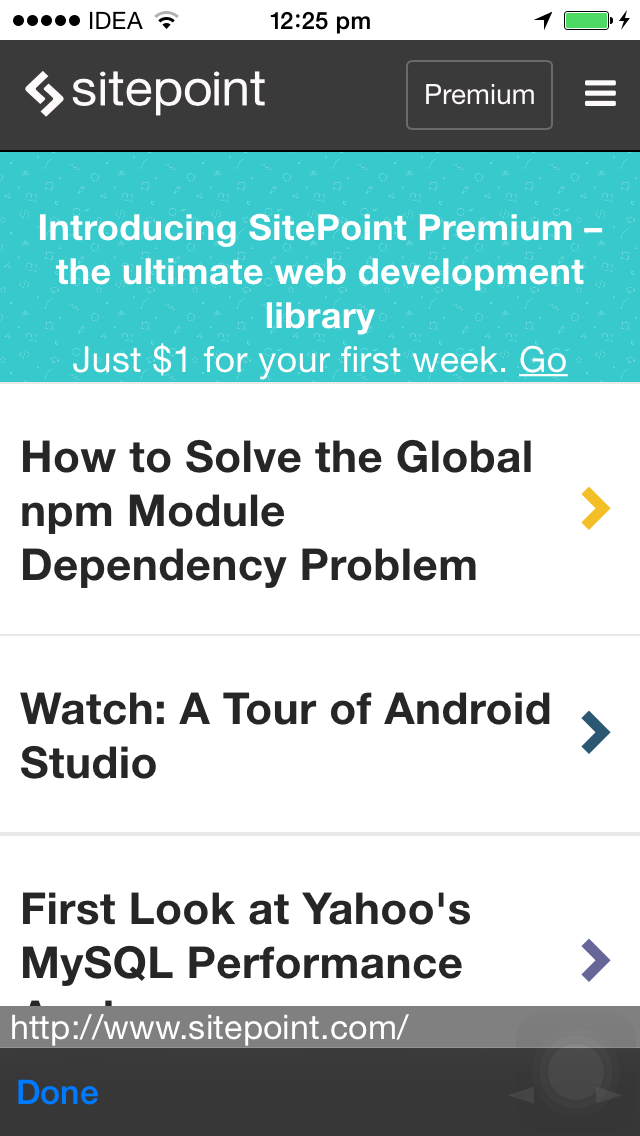
}Before the page is rendered, we populate the table with local data. When a URL is clicked we invoke the openURL function which opens the URL in an InAppBrowser window.
Here is how the page now looks:
This is how the InAppBrowser window looks:
Conclusion
This tutorial was a basic introduction to reading a barcode with a Cordova app. We learned how to distinguish between different barcode types, the plugins that can help us and how to scan and store barcodes.
Let me know your experiences trying this tutorial and ideas for expanding it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Scanning QR Code with Cordova
How can I install the Cordova QR code scanner plugin?
To install the Cordova QR code scanner plugin, you need to have Node.js and npm installed on your system. Once you have these, you can install Cordova by running the command npm install -g cordova in your terminal. After Cordova is installed, you can add the QR code scanner plugin by running the command cordova plugin add cordova-plugin-qrscanner. This will install the QR scanner plugin in your Cordova project.
How can I use the Cordova QR code scanner plugin in my application?
After installing the Cordova QR code scanner plugin, you can use it in your application by calling the cordova.plugins.barcodeScanner.scan function. This function takes a success callback function, an error callback function, and an options object as parameters. The success callback function is called when a QR code is successfully scanned, and the error callback function is called when there is an error scanning the QR code.
What are the options I can pass to the scan function?
The scan function takes an options object as the third parameter. This object can have the following properties: preferFrontCamera (a boolean indicating whether to use the front camera for scanning), showFlipCameraButton (a boolean indicating whether to show a button to flip the camera), showTorchButton (a boolean indicating whether to show a button to toggle the torch), prompt (a string to show as a prompt), formats (a string specifying the formats to scan), orientation (a string specifying the orientation of the scan), and disableAnimations (a boolean indicating whether to disable animations).
How can I handle the result of a successful scan?
The success callback function passed to the scan function is called with a result object when a QR code is successfully scanned. This object has the following properties: text (the text encoded in the QR code), format (the format of the scanned code), and cancelled (a boolean indicating whether the scan was cancelled).
How can I handle errors while scanning a QR code?
The error callback function passed to the scan function is called with an error message when there is an error scanning a QR code. You can use this function to handle any errors that occur while scanning a QR code.
Can I use the Cordova QR code scanner plugin to scan barcodes as well?
Yes, the Cordova QR code scanner plugin can also scan barcodes. You can specify the formats to scan in the options object passed to the scan function. The formats can be a comma-separated list of formats, and the supported formats include QR_CODE, DATA_MATRIX, UPC_E, UPC_A, EAN_8, EAN_13, CODE_128, CODE_39, CODE_93, CODABAR, ITF, RSS14, RSS_EXPANDED, PDF_417, and AZTEC.
Can I use the Cordova QR code scanner plugin in a Cordova-based framework like Ionic or PhoneGap?
Yes, the Cordova QR code scanner plugin can be used in any Cordova-based framework like Ionic or PhoneGap. You can install the plugin in the same way as in a Cordova project, and use it in the same way as well.
How can I test the Cordova QR code scanner plugin in a browser?
The Cordova QR code scanner plugin cannot be tested in a browser because it uses native device capabilities that are not available in a browser. You need to test it on a real device or an emulator.
Can I customize the appearance of the scanner?
The appearance of the scanner is determined by the native scanning library used by the plugin, and cannot be customized directly from the plugin. However, you can customize the prompt shown to the user by setting the prompt property in the options object passed to the scan function.
What should I do if the scanner is not working?
If the scanner is not working, you should first check if you have correctly installed the plugin and correctly used the scan function. If everything is correct, you should check the error message passed to the error callback function to see what the problem is. If you still cannot solve the problem, you can ask for help on the plugin’s GitHub page or on Cordova’s community forums.
 Narayan Prusty
Narayan PrustyNarayan is a web astronaut. He is the founder of QNimate. He loves teaching. He loves to share ideas. When not coding he enjoys playing football. You will often find him at QScutter classes.

